As innovators in the hosting space, we’re constantly testing hardware and software solutions here at Pagely to find the optimum balance between price and performance for the unique demands of WordPress.
Through all of that testing, Amazon RDS emerged as the clear winner for our database solution. We’ve built our hosting solution on it so it’s fair to say we’re fans. In this post we’ll give an overview of RDS, how it works, and its features and benefits.
For us, as it does for many other businesses, it comes down to a mixture of reliability, flexibility, and, most importantly of all, it integrates seamlessly with the powerful AWS cloud ecosystem.
What is RDS?
When Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) burst onto the scene in 2009, it was immediately hailed as a game-changer. It was a revolutionary “database as a service” solution that made it simple and easy to set up, manage, and scale a database that included built-in scalability, redundancy, and failover protection.
One of its biggest innovations was separating the database from the server. “When you buy a server, you get CPU, memory, storage, and IOPS, all bundled together. With Amazon RDS, these are split apart so that you can scale them independently. If you need more CPU, less IOPS, or more storage, you can easily allocate them.” Source
RDS is a managed solution so you won’t have shell access and there’s restricted access on advanced privileges but the majority of what you would need to do is handled for you so this is a non-issue in most cases.
RDS versus other cloud database solutions
When it comes to cloud database solutions, AWS is the industry leader by a landslide:
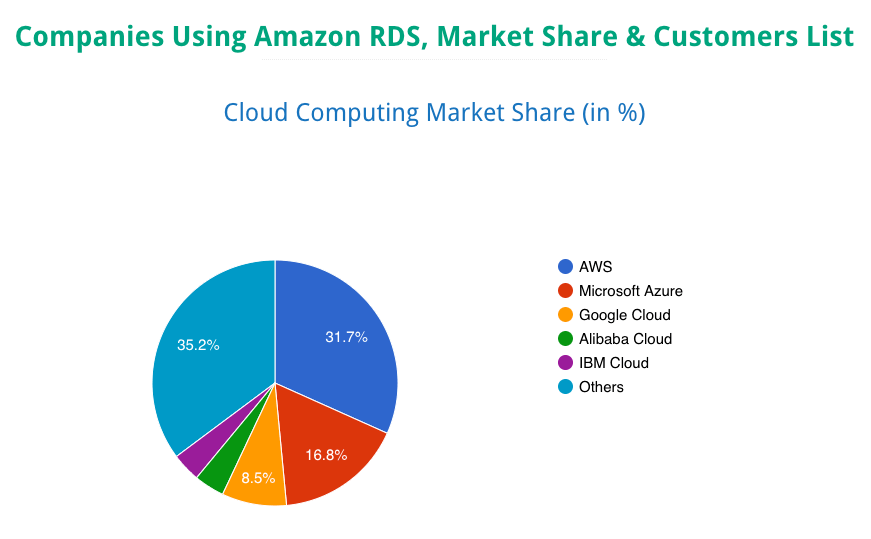
While alternatives from Google, Microsoft, Oracle, and IBM exist, they have not become as popular in spite of aggressive pricing aimed at stealing market share from AWS.
RDS’s preeminent advantage over other cloud database solutions is that it integrates seamlessly with AWS’s robust ecosystem of cloud-based tools, services, and solutions. AWS is far and away the leading cloud provider with the most powerful, reliable, and flexible suite of cloud services that integrate flawlessly with one another.
Today, Amazon offers an incomparable array of over 170 cloud services and continuously introduces more to complement existing services and add new functionality:
- EC2 Instances
- Amazon Simple Storage Solution (S3)
- Amazon Aurora
- AWS Lambda
- Amazon LightSail
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
- Amazon Route 53
- See the full list of services here
Cloud services like these have become the building blocks of the internet as we know it today. These services can be combined to create powerful new solutions that are greater than the sum of their parts, like our Managed WordPress Hosting.
How does RDS work?
RDS operates within an instance (an isolated, cloud-based database environment). When you create a new database, you choose the database engine it runs.
RDS is compatible with the most popular engines:
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- PostgreSQL
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Aurora
The computation and memory resources allocated to the database are determined by what AWS calls its “instance class.” As a database grows, its instance class can easily be upgraded with very little downtime to provide more resources making it a highly scalable and flexible solution.
There are currently 27 instance classes to choose from with a range of resource options. Instances can have as little as 1 GB of memory up to 256 GB and provide a single processing core up to 64 cores. There’s an instance class to fit pretty much every use case and all of these instance sizes are available to Pagely customers so RDS is part of what makes Pagely such a flexible, customizable hosting solution for companies with unique technical demands.
High availability
For enterprises that rely on their databases, one of the most important features offered by RDS is its Multi-AZ (Multiple Availability Zone) option. Two distinct copies of the database are created — a primary that handles read and write requests and a secondary that is only written to. If there is an availability issue, the secondary database is promoted into the primary role and the traffic is re-routed using DNS.
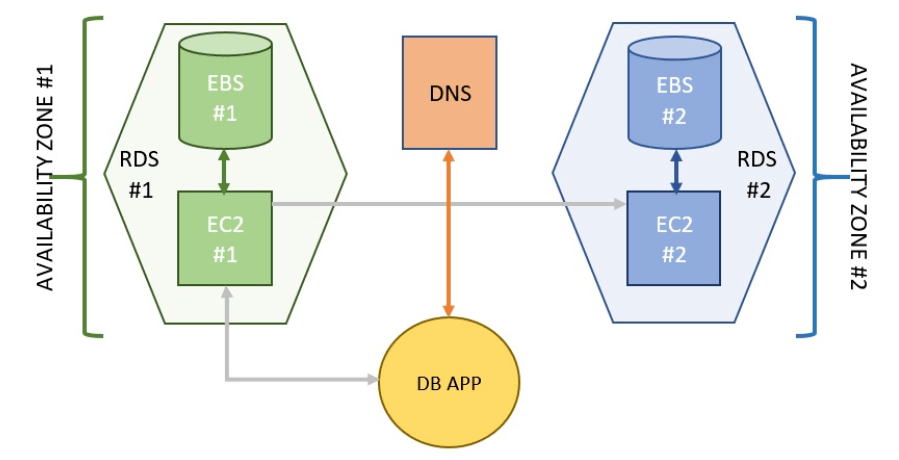
It’s important to note that the Multi-AZ feature is not a scaling solution because the secondary database cannot serve read traffic. For scaling, Amazon has Read Replicas.
Read Replicas
Using Read Replicas “you can elastically scale out beyond the capacity constraints of a single DB instance for read-heavy database workloads.” Source
To get started with Read Replicas you first pick a database that will operate as the source. A snapshot is created to duplicate the database and that duplicate version is updated whenever there is a change to the source database.
Note that Read Replicas are only compatible with MariaDB, MySQL, Oracle, and PostgreSQL engines.
Benefits of RDS
RDS’s feature set makes it an attractive database solution:
A managed solution
AWS takes care of backups, software patching, automatic failure detection, and recovery so your administrative burden is close to nil. They have a nearly impeccable track record in this department so you can rest easy knowing your database is being managed by experts.
High performance
RDS uses Solid State Drives (SSDs) to achieve high input/output (IO) throughput and also has an option for Provisioned IOPS (SSD) Storage, which allows you to specify a target input/output operations per second (IOPS) rate when creating the database instance.
Scalability
RDS users can easily and quickly scale their compute and storage resources with very little downtime. They also offer read replicas that allow users to scale out read-heavy databases.
Superior availability and durability
RDS offers automated backups for point-in-time recovery for a user-specified retention period. This means you can restore to literally any second within the retention period. In the event of a hardware failure, AWS will automatically replace the hardware on that compute instance.
Robust security
If an instance is running with RDS encryption, the data, its backups, replicas, and snapshots are all encrypted and SSL is used to encrypt data in transit. Resource-level permissions give granular control over who has access to the database and what capabilities they have.
Manageability
Amazon CloudWatch is included so you’ll have detailed analytics on your databases’ performance at no additional charge. You can receive text and email alerts through Amazon SNS. AWS Config records and audits changes to the database config to support governance and compliance needs. Amazon’s Performance Insights makes analyzing performance data to tune your database easier than ever.
If you’re already using the AWS ecosystem, there’s no compelling reason to choose anything else. Even if you’re not, the RDS solution offers a superior feature set, with a much longer track record of reliability, than competing solutions.
Amazon RDS offers many advantages over traditional database solutions. It’s flexible, reliable, and easily manageable. If you’re researching RDS for WordPress website hosting, you may want to consider a Managed WordPress Hosting solution that uses RDS, like Pagely.
Pagely masks the complexity and eliminates the time costs associated with managing your own database and server. If you’re interested in hassle-free WordPress hosting powered by AWS infrastructure and optimized by a team of WordPress hosting experts, start a discussion with our sales team or see our plans and sign up here.